概要
JavaScriptでは非同期処理を管理するためにPromiseを使用します。
このPromiseの仕組みを下記ブログで書いたようにes6-promiseをコードリーディングをして、理解していきました。 本記事ではそれを踏まえて自前で簡易的なPromiseの機能を実装していきたいと思います。
https://zenn.dev/daiju81/articles/f904c16384a02e
状態管理
まずはes6-promiseにもあるように状態管理用の変数を定義、初期化するコードを書いていきます。
また、thenメソッドで渡された関数を保存しておく配列も用意しておきます。
const PENDING = void 0;
const FULFILLED = 1;
const REJECTED = 2;
constructor(resolver) {
this._result = this._state = undefined;
this._FulfilledSubscribers = [];
this._RejectedSubscribers = [];
}
非同期処理実行
ユーザーが渡した関数(resolver)を実行して、うまくいけばresolve、失敗したらrejectを実行するコードを書きます。
try {
resolver(resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
state更新と成功/失敗後にキューに保存された関数を実行
それぞれのresolve, reject関数で、state, resultを更新して、その後にキューに保存された関数をforEach文で実行していきます。
const resolve = (value) => {
this._state = FULFILLED;
this._result = value;
this._FulfilledSubscribers.forEach((callback) => callback(this._result));
};
const reject = (value) => {
this._state = REJECTED;
this._result = value;
this._RejectedSubscribers.forEach((callback) => callback(this._result));
};
キューに関数を保存するthenメソッド
成功or失敗していたら、そのまま、onFulfilled, onRejectedを実行する、どちらでもなければ、配列(キュー)に保存して、成功or失敗後に実行するコードを書きます。
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this._state === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this._result);
} else if (this._state === REJECTED) {
onRejected(this._result);
} else {
this._FulfilledSubscribers.push(onFulfilled);
this._RejectedSubscribers.push(onRejected);
}
}
実際に使用してみる
下記のようにコードを使用してみます。
const myPromise = new OriginalPromise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve("Success");
}, 3000);
});
myPromise.then(
(value) => {
console.log(`resolved1: ${value}`);
},
(value) => {
console.log(`rejected1: ${value}`);
}
);
myPromise.then(
(value) => {
console.log(`resolved2: ${value}`);
},
(value) => {
console.log(`rejected2: ${value}`);
}
);
下記を見ると成功して、しっかりログが出力されていることがわかります。
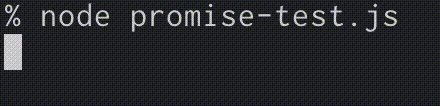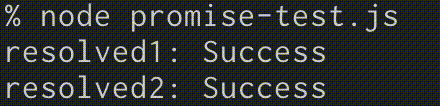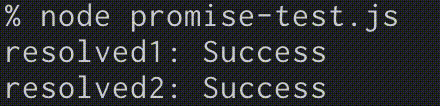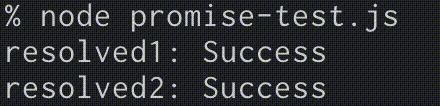
コード完全版
const PENDING = void 0;
const FULFILLED = 1;
const REJECTED = 2;
class OriginalPromise {
constructor(resolver) {
this._result = this._state = undefined;
this._FulfilledSubscribers = [];
this._RejectedSubscribers = [];
const resolve = (value) => {
this._state = FULFILLED;
this._result = value;
this._FulfilledSubscribers.forEach((callback) => callback(this._result));
};
const reject = (value) => {
this._state = REJECTED;
this._result = value;
this._RejectedSubscribers.forEach((callback) => callback(this._result));
};
try {
resolver(resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this._state === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this._result);
} else if (this._state === REJECTED) {
onRejected(this._result);
} else {
this._FulfilledSubscribers.push(onFulfilled);
this._RejectedSubscribers.push(onRejected);
}
}
}
まとめ
PromiseはJavaScriptで非同期処理を扱う際に重要な仕組みです。 自前実装することで内部動作を少し理解することができました。